Reaction of Carboxylic Acids with Alcohols
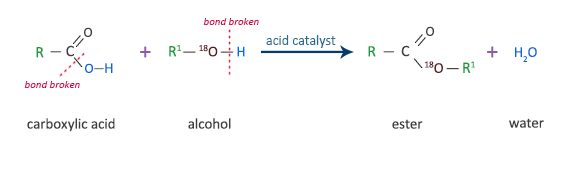
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to form esters. This type of reaction is called esterification.
 ester + water
ester + waterThe diagram below shows the bridging oxygen for the ester comes from the alcohol. This was determined by the American chemists Irving Roberts and Harold C. Urey in 1938, using a technique called isotopic labelling. This method involves preparing an alcohol with the oxygen isotope 18O for reaction with a carboxylic acid. Analysis of the reaction products in a mass spectrometer shows that all the 18O is in the ester and not in the water. Therefore, all the bridging oxygen must come from the alcohol.
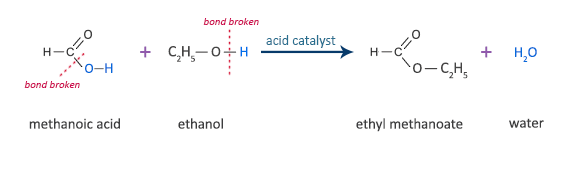
Methanoic Acid Reaction with Ethanol
methanoic acid + ethanol  ethyl methanoate + water
ethyl methanoate + water
HCOOH + C2H5OH  HCOOC2H5 + H2O
HCOOC2H5 + H2O
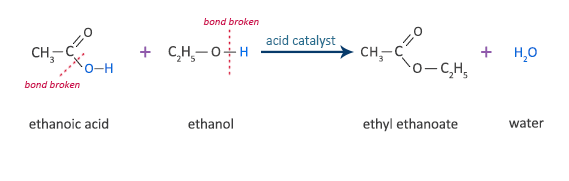
Ethanoic Acid Reaction with Ethanol
ethanoic acid + ethanol  ethyl ethanoate + water
ethyl ethanoate + water
CH3COOH + C2H5OH  CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
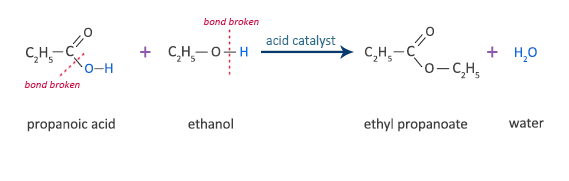
Propanoic Acid Reaction with Ethanol
propanoic acid + ethanol  ethyl propanoate + water
ethyl propanoate + water
C2H5COOH + C2H5OH  C2H5COOC2H5 + H2O
C2H5COOC2H5 + H2O
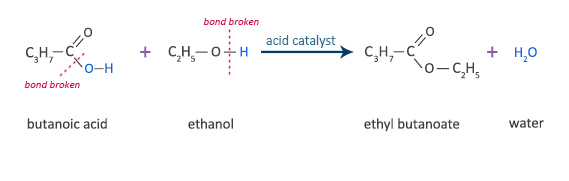
Butanoic Acid Reaction with Ethanol
butanoic acid + ethanol  ethyl butanoate + water
ethyl butanoate + water
C3H7COOH + C2H5OH  C3H7COOC2H5 + H2O
C3H7COOC2H5 + H2O