Reaction of Carboxylic Acids with Carbonates
Carboxylic acids react with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to form a salt, carbon dioxide and water.
The hydrogen in the hydroxyl part of the carboxylic group is lost and replaced with the metal of the salt. For example in the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium carbonate:
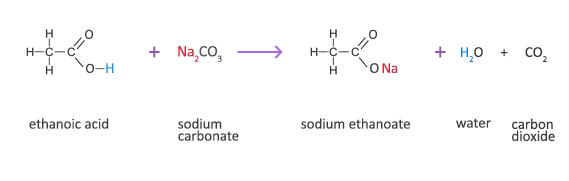
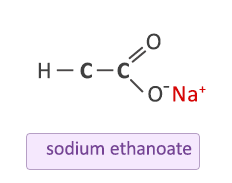
The equation above is unbalanced but shows the hydrogen (blue) in the hydroxyl part of the carboxylic group is lost and replaced by the sodium (red). The resulting bond between the sodium and the ethanoate group is ionic. It must not be represented by a line between the two atoms as this would represent a covalent bond.
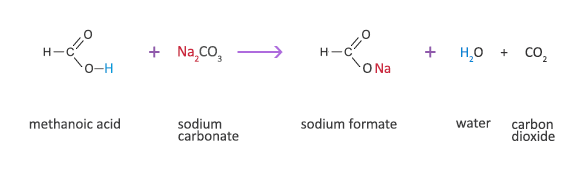
Methanoic Acid Reaction with a Carbonate
Methanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium formate + water + carbon dioxide
2HCOOH(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2HCOONa(aq) +H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Ethanoic Acid Reaction with a Carbonate
Ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium ethanoate + water + carbon dioxide
2CH3COOH(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2CH3COONa(aq) +H2O(l) + CO2(g)

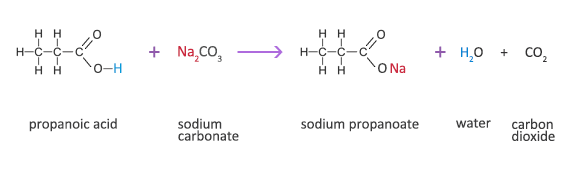
Propanoic Acid Reaction with a Carbonate
Propanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium propanoate + water + carbon dioxide
2C2H5COOH(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2C2H5COONa(aq) +H2O(l) + CO2(g)
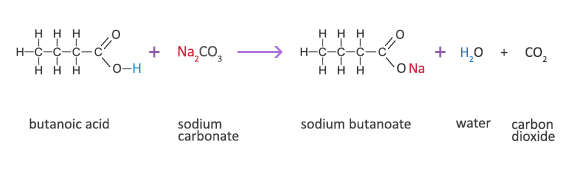
Butanoic Acid Reaction with a Carbonate
Butanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium butanoate + water + carbon dioxide
2C3H7COOH(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2C3H7COONa(aq) +H2O(l) + CO2(g)